Selecting between CPU and GPU server infrastructure isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a foundational element that shapes your organization’s ability to deliver on advanced workloads, operational efficiency, and digital innovation goals. This in-depth review explores the architectural, performance, and strategic distinctions between CPU and GPU servers, using XLC’s enterprise-grade solutions as reference points for demanding, data-driven environments.
Key Takeaways
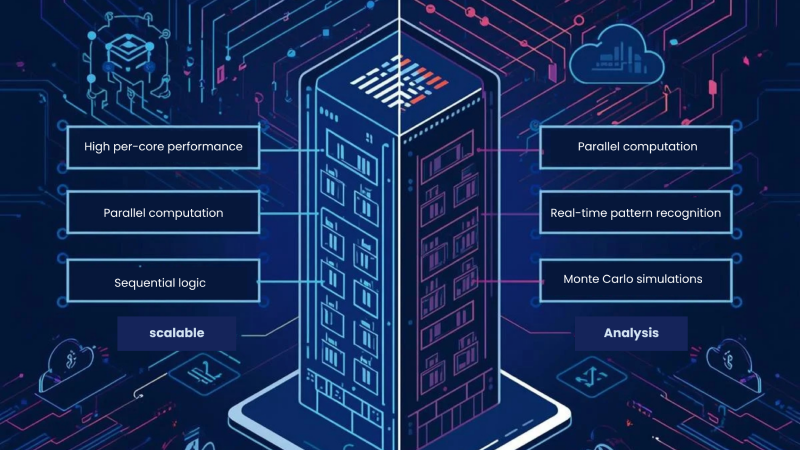
- Architectural Distinction: CPUs are optimized for sequential, logic-intensive workloads, while GPUs deliver massive parallelism, accelerating AI, analytics, and rendering.
- Workload Alignment: CPU servers excel at virtualization, database management, and high-frequency trading; GPU servers unlock new capabilities for machine learning, big data, and 3D visualization.
- Configurable Performance: XLC’s offerings allow tailored deployments—from high-frequency AMD EPYC compute nodes to multi-GPU NVIDIA RTX clusters—matching business needs and growth trajectories.
- Scalability and Network Reach: Global data centers and advanced network engineering enable ultra-low latency and high throughput for cross-border and real-time workloads.
- Compliance and Security: Robust DDoS protection, ISO 27001, SOC2, and PCI DSS certifications support regulated industries and sensitive applications.
CPU vs GPU: Architecture and Application Deep Dive
CPUs (Central Processing Units) remain the “generalists” of server infrastructure, designed for flexibility and low latency in a wide range of business applications. Modern CPUs, like AMD EPYC and Intel Xeon, offer multiple high-speed cores, ECC DDR5 memory, and advanced instruction sets such as AVX-512 for vectorized workloads. XLC’s bare metal CPU server lineup demonstrates how these features translate into tangible benefits for ERP systems, virtualization clusters, and transactional databases.GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), by contrast, are specialists in parallel computation. Featuring thousands of lightweight cores, GPUs such as NVIDIA’s RTX 4090 or H100 are built to execute the same operation across massive datasets—ideal for deep learning, scientific simulations, and high-resolution rendering. XLC’s dedicated GPU servers leverage this technology to power demanding AI projects, big data analytics, and immersive media experiences.
Table: XLC Server Configurations for CPU vs GPU Workloads
| Model | CPU(s) | RAM | Storage | GPU (Max) | Ideal Workload | Starting Price (USD/mo) |
| AMD EPYC 4464P | 12 Cores, 24 Threads | 32GB DDR5 | 960GB NVMe Gen4 SSD | N/A | Database, Virtualization, Web Hosting | $139 |
| AMD EPYC 4584PX | 16 Cores, 32 Threads | 64GB DDR5 | 960GB NVMe Gen4 SSD | N/A | Fintech, SaaS, eCommerce | $209 |
| AMD EPYC 7402P | 24 Cores, 48 Threads | 64GB DDR4 | 960GB NVMe Gen4 SSD | Up to 4x RTX 4090 | AI Training, 3D Rendering, Analytics | $559 |
| Dual AMD EPYC 7313 | 32 Cores, 64 Threads | 128GB DDR4 | 960GB NVMe Gen4 SSD | Up to 8x RTX 4090 | Deep Learning, Simulation, Scientific Research | $809 |
| Dual AMD EPYC 7B13 | 64 Cores, 128 Threads | 128GB DDR4 | 960GB NVMe Gen4 SSD | Up to 8x RTX 4090 | Multi-modal AI, High-Performance Computing | $879 |
Tip: Align the memory and GPU VRAM to your application’s dataset size and computational requirements. Multi-GPU configurations are particularly effective for distributed AI model training and large-scale simulations.
Performance Insights and Strategic Fit
Industry analysis and third-party benchmarks consistently show that GPU servers outperform CPUs by orders of magnitude on parallel workloads—such as neural network training, image processing, and real-time analytics. For example, XLC’s NVIDIA RTX 4090 GPU servers can deliver up to 50x faster AI model training compared to CPU-only platforms, reducing time-to-insight and accelerating innovation cycles.Conversely, high-frequency CPU servers are indispensable for sequential tasks, such as high-frequency trading, web serving, or complex business logic where per-core performance and latency are paramount. XLC’s customizable CPU nodes, with options for up to 256 cores and advanced memory bandwidth, are engineered to support multi-tenant environments, transactional workloads, and business-critical applications.
Table: CPU vs GPU Server Application Alignment
| Application Area | CPU Server Strengths | GPU Server Strengths |
| Virtualization | High per-core performance | Not optimal |
| AI/ML Training | Data prep, orchestration | Model training, inference, deep learning |
| Big Data Analytics | ETL, transaction processing | Pattern recognition, real-time analytics |
| Rendering/Visualization | Logic, timeline edits | 3D rendering, ray tracing, video encoding |
| Scientific Computing | Simulation setup, control | Parallel computation, simulation acceleration |
| Financial Modeling | Sequential math, OLTP | Monte Carlo, risk modeling |
Tip: For hybrid workloads, consider XLC’s bare metal platforms with both high-frequency CPUs and dedicated GPUs—delivering versatility for rapidly evolving business needs.
Network, Security, and Compliance
XLC’s global data center footprint—spanning Los Angeles, Tokyo, and Hong Kong—offers direct connectivity to Tier 1 carriers and Asia-Pacific networks, supporting ultra-low latency and stable cross-border operations. Advanced engineering, such as BGP traffic management, dual power feeds, and N+1 cooling, ensures high availability and business continuity even during regional disruptions.Security and compliance are pivotal. XLC’s infrastructure includes always-on DDoS mitigation, hardware-level protections, and adherence to leading certifications (ISO 27001, SOC2, PCI DSS). This supports regulated industries, from fintech to healthcare, and ensures data sovereignty with localized hosting options.
Operational Flexibility and Support
Self-service management portals, automated provisioning, and 24/7 expert support empower organizations to scale dynamically—whether deploying new AI models, expanding SaaS platforms, or responding to sudden traffic spikes. XLC’s transparent, commitment-free pricing protects your budget, while rapid 1-hour deployments enable swift adaptation to market opportunities.
Tip: Leverage benchmarking on test servers before full-scale deployment to ensure optimal resource allocation and cost efficiency.
FAQ
What workloads benefit most from GPU servers at XLC?
GPU servers are ideal for AI model training, deep learning, 3D rendering, scientific research, and real-time analytics where parallelism is critical.
Are hybrid CPU+GPU servers available?
Yes, XLC offers configurable platforms with high-frequency CPUs and multiple GPUs, supporting hybrid analytics, simulation, and AI workloads.
How fast can XLC provision a server?
Most in-stock configurations are provisioned within 1 hour. Custom multi-GPU builds are available for pre-order and rapid deployment.
Does XLC support compliance for regulated industries?
Absolutely. XLC’s infrastructure is certified for ISO 27001, PCI DSS, and SOC2, supporting financial, healthcare, and data-sensitive applications.
Is there a minimum commitment or hidden fee?
No. XLC provides clear, contract-free terms and flexible scaling—pay only for what you use.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between CPU and GPU server architectures enables organizations to architect the right foundation for modern business applications. CPUs remain essential for sequential logic and virtualization, while GPUs unlock transformative acceleration for AI, analytics, and visualization. With XLC’s global infrastructure, advanced hardware, and expert support, enterprises are empowered to meet today’s most complex computing challenges—scaling with confidence and agility as digital transformation accelerates.For tailored advice or a trial deployment, connect with XLC and explore how the right mix of CPU and GPU infrastructure can drive your business forward.